The baby has a long-awaited event in every loving family, which is accompanied not only by sleepless nights, but also by worries about the well-being of the crumbs. By the age of three, a child should already have a full set of 20 temporary teeth, which will begin to fall out at about the age of five. They will be replaced by new permanent teeth that will accompany the child throughout his life. Caring parents should pay increased attention to this process and study all the nuances in advance.
Scheme of eruption of milk teeth
At the age of 2.5-3 years, 10 milk teeth are symmetrically located on the lower and upper jaws of the child:
- 4 molars (2 on each side);
- a pair of fangs;
- a pair of lateral incisors;
- 2 central incisors.

Important! In some cases, the baby may have a congenital pathology, which consists in the absence of the rudiments of one or more milk teeth. It can only be detected closer to 15 months.
Table. What does the process of eruption of the first teeth look like.
| Jaws | Name of the tooth | Eruption period |
|---|---|---|
| Pair of incisors (central) | 6-10 months |
|
| Pair of incisors (lateral) | 10-16 months |
|
| Lower jaw | 2 fangs | 17-23 months |
| Left and right second molars | 14-18 months |
|
| First pair of molars | 23-31 months |
|
| 2 central incisors | 0-12 months |
|
| Pair of lateral incisors | 9-13 months |
|
| upper jaw | 2 fangs | 16-22 months |
| Left and right second molars | 13-19 months |
|
| First pair of molars | 25-33 months |
It should be noted that these dates do not always coincide with the real ones. It is not uncommon for milk teeth to erupt in a non-standard order, one or even two pairs at a time. You should not be afraid of this, as each child develops at his own pace.
What teeth do children change
Among some parents, there is an opinion that pairs of first and second molars, erupting already closer to the 3rd year, are indigenous and should not be replaced. It is erroneous, all the 20 first teeth of the child are milk. However, in medical practice, many cases have been recorded when people live to old age with 1 or even 2 pairs of milk molars. This anomaly can be both acquired (in case of injury to the molar in the rudiment), and congenital hereditary nature.
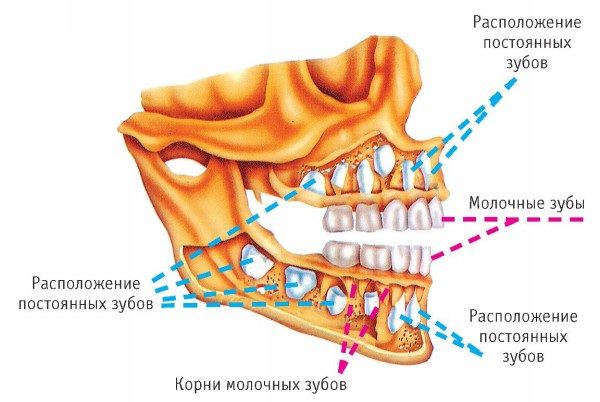
Important! Loss of milk teeth occurs only in the case of resorption of temporary roots under the pressure of a permanent tooth.
When should temporary teeth fall out?
As for the eruption process, there are medical standards for the timing of the normal change of milk teeth to molars.
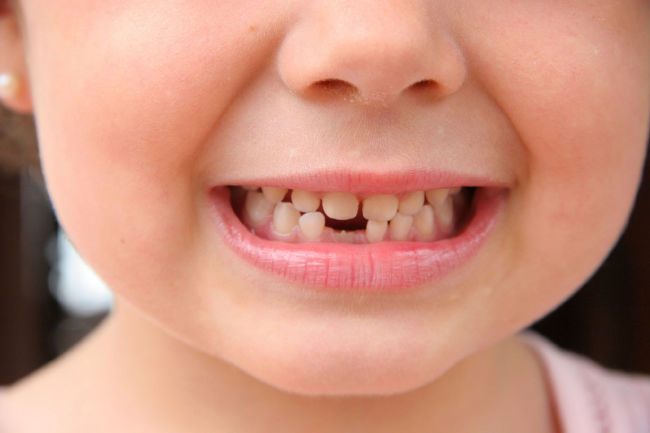
Table. The procedure for changing milk teeth to permanent ones.
| Name of the tooth | Root resorption period | Drop dates |
|---|---|---|
| Upper and lower central incisors | From 5 to 7 years old | About 6-7 years old |
| Upper and lower lateral incisors | From 6 to 8 years old | About 7-8 years old |
| Upper and lower small molars | From 7 to 10 years old | About 8-10 years old |
| Upper and lower fangs | 8 to 11 years old | About 9-11 years old |
| Upper and lower large molars | From 7 to 10 years old | About 11-13 years old |
The starting point for starting the process of replacing a temporary set of teeth is the eruption of 2 pairs of permanent (third) molars. Most often this happens at the age of 4 years, however, in each baby, the first molars can appear either a little earlier than the due date, or later. Over the next year, you can see with the naked eye a change in the shape of the child's jaw. Due to the growth of the jaw bones, the space between the teeth increases markedly.
Attention! The process of physiological maturation in girls is faster than in boys. This fact directly affects the timing of the change of temporary teeth.

How timely teeth fall out and grow depends on many factors, namely:
- hereditary predisposition of the child to early or late change of teeth;
- variety of foods in the child's diet;
- drinking water quality;
- frequent stress;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the child.

Early late tooth loss: causes and consequences
- abnormal bite;
- forced surgical removal of teeth due to caries;
- nearby growing neoplasm;
- if there is excessive pressure on the tooth from neighboring ones;
- injury.
With early loss of teeth, the so-called natural spatial balance is disturbed. The fact is that the position of milk teeth directly affects the formation of the root jaw in a child. During eruption, permanent teeth tend to hatch in the place of least gum resistance, that is, where there is a wound that has not completely hardened from the loss of milk bone formation. If the tooth falls out before the beginning of the movement of the root, the risk of the formation of not only, but also an abnormal shift of the teeth relative to each other, is significantly increased.
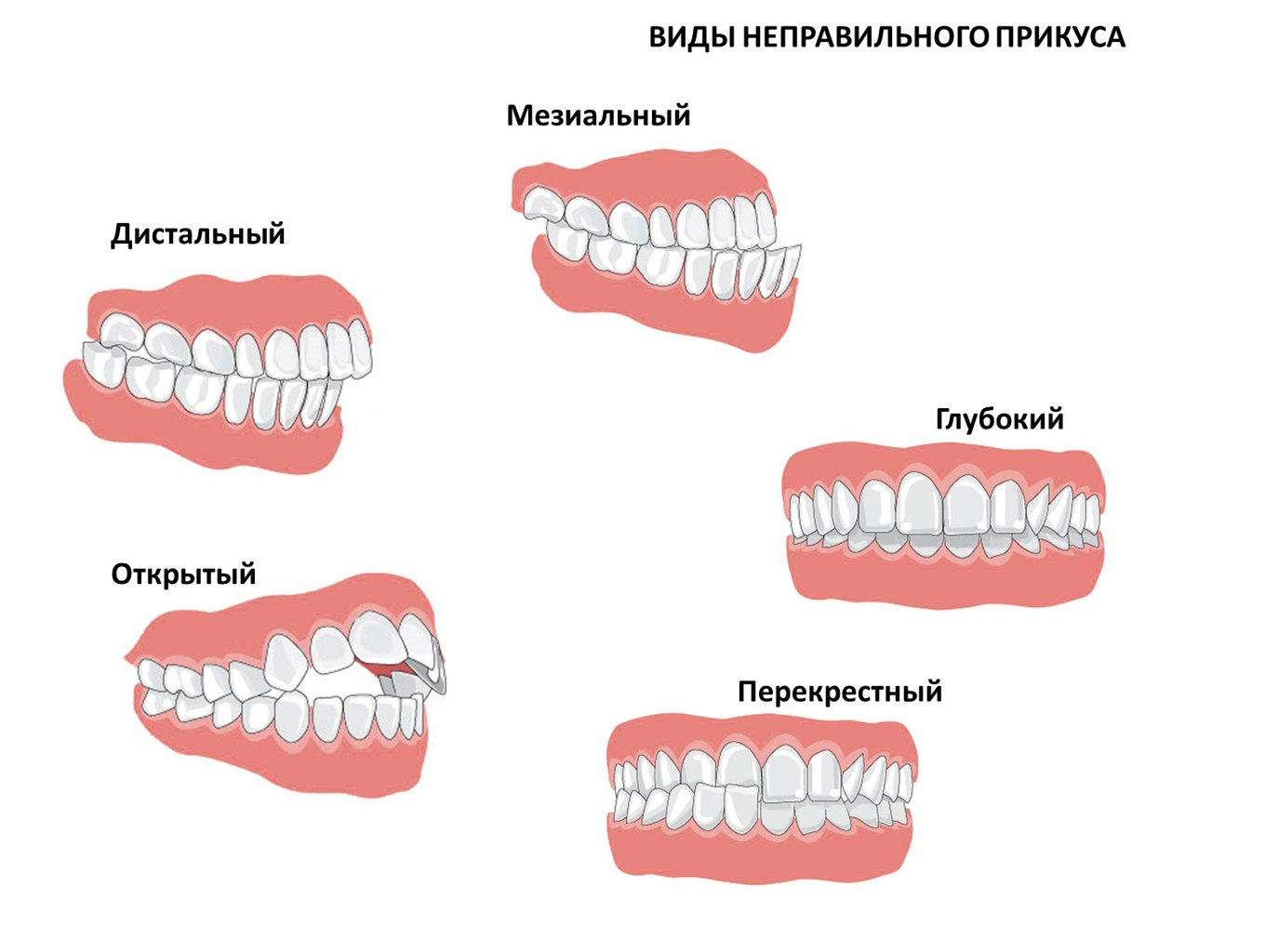
Late tooth loss also entails risks of improper jaw formation. This phenomenon is influenced by a number of factors:
- the genetic predisposition of the child to the late change of milk teeth;
- rickets;
- severe infectious disease.
Attention! If an eight-year-old child does not have any signs of temporary teeth falling out, be sure to consult a pediatric dentist.

Sometimes a milk tooth begins to loosen in accordance with the standard dental terms for changing temporary teeth, but the root does not have time to dissolve in time. As a result, a new permanent tooth grows next to the old one, thereby forming a parallel row of "shark" teeth. You should not be afraid of this. In most cases, as the milk bone formations fall out, the molars will move to their normal position.
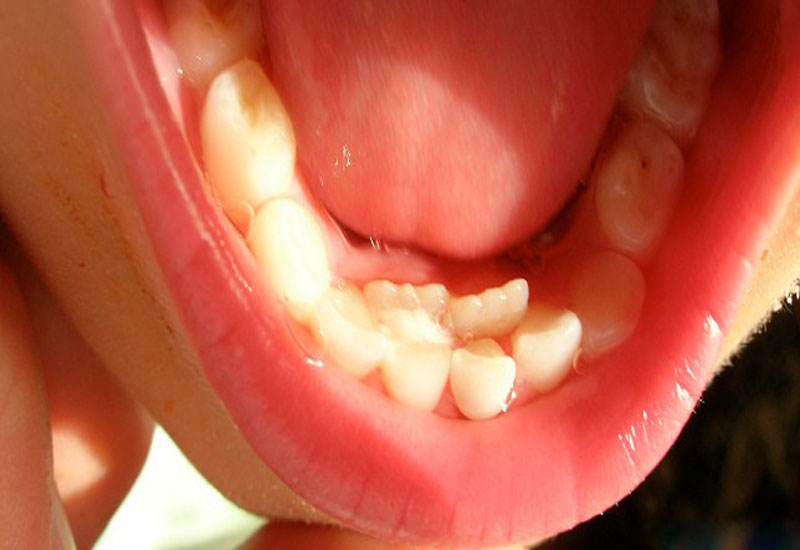
When do you need to seek special medical care?
As it may seem at first glance, the loss of milk teeth cannot be accompanied by serious complications. However, some symptoms require the mandatory intervention of specialists.
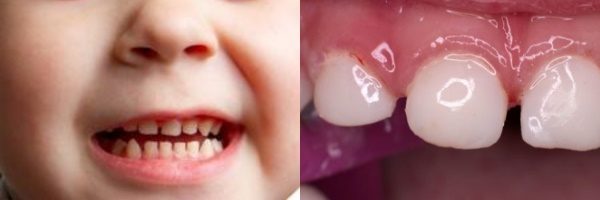
Medical assistance is needed in the following situations.
- The child has a loose milk tooth for several weeks or even months, but there are no signs of loss. In this case, it is necessary to pull out a temporary bone formation to ensure unhindered growth of the molar tooth.
- If the baby has severe swelling of the gums during the eruption of a permanent tooth, the child experiences severe pain, an emergency examination of the dentist will be required.
- When a baby tooth falls out, a bleeding wound forms in the gum. You need to contact a specialist if the bleeding does not stop for more than 10 minutes. This may indicate the presence of diseases that affect the function of blood clotting.
- The child complains about the molar.

Important! As soon as the baby's tooth fell out, it is necessary to attach a sterile swab to the wound and ask the child to squeeze his jaw. Normally, bleeding should stop after 5-10 minutes.
Nutrition of the child during the period of change of milk teeth
At the age of 5-13 years, when permanent teeth are formed, the child needs an additional source of vitamins and microelements. The daily diet should include the following foods.


Carefully! Uncontrolled consumption of sweets by a child can lead not only to dental problems, but also to diabetes.
Oral hygiene during the period of loss of milk teeth
At the age of 5 years, the child is not yet able to take care of his teeth and oral cavity to the full extent. Therefore, parents should know the basic rules that must be observed during the growth of molars.

The formation of a snow-white smile in a child is a protracted process that requires maximum attention from the parents, because the molars will be with the child all his life.