Medicine has achieved good results in the field of artificial insemination. Unfortunately, pregnancy with IVF does not occur in every woman. In order to understand what embryonic hatching is in IVF, experts explain the process of an embryo emerging from its shell.
Purpose of the procedure
Assisted hatching before embryo transfer involves cutting the shell to increase the chance of conception. The natural process of the exit of the embryo from the shell often ends in failure, and the reasons are its thickening or hardening.
The process is carried out under a microscope, the doctor makes a small incision on the shell, and then introduces a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. Thus, specialists help the embryo to attach for the further development of the fetus.
Embryo hatching is an event to release the shell in order to attach to the wall of the uterus. Problems with this action often lead to female infertility. The purpose of this procedure is to eliminate the problem associated with the exit from the shell of a fertilized embryo.
IVF hatching is used in exceptional cases, and is not included in the main program of artificial insemination.
Under natural conditions, the egg after fertilization leaves the shell on the 5th day. In the interval between fertilization and attachment of the embryo to the uterus, assisted hatching is used.
Indications for the procedure
In the treatment of infertility, in some cases, hatching of embryos is used for medical reasons.
- age over 38 years;
- violation of natural hatching;
- a sufficiently high thickness of the shell and other anomalies in its development;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- bad habits;
- unsuccessful IVF attempts;
- the level of FSH in the patient's blood is increased;
- follicle-stimulating hormone exceeds the norm;
- cryopreservation of oocytes and embryos.
A contraindication to the use of such a micro-operation is the situation when the blastomeres (embryo cells) do not pass into meiotic interphase 1. The process is performed only by specialists in clinics equipped with modern equipment.
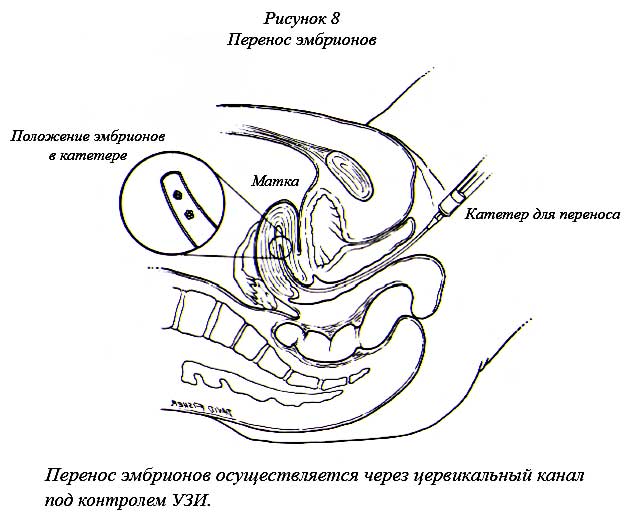
Hatching in the eco program is not initially provided as a mandatory procedure. A woman who is shown this operation needs to understand its importance for a positive result.
If a woman has had two or more unsuccessful attempts at IVF fertilization, doctors prescribe a special procedure for assisted hatching, performed according to one of the methods. This greatly increases the likelihood that the implantation of the embryo will be successful, and the female body will accept the fertilized egg.
Execution Methods
Hatching after cryofreezing will allow several times to increase the chance of successful implantation of the embryo in the uterus and the onset of pregnancy in a woman who decides on IVF. Cryotransfer hatching is performed in several ways.
Each method has its own characteristics and disadvantages:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- laser;
- piezo technique.
Mechanical. In this case, the specialist cuts the shell manually using a microscopic needle. The puncture is made at a certain angle, due to which a small slot is formed. This technique has practically no complications.
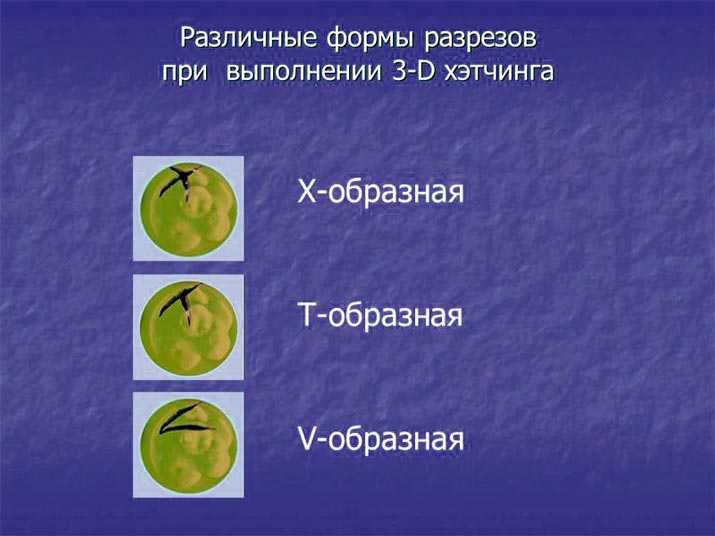
Chemical. This method involves the use of a special chemical solution called Tyrode, which corrodes the shell. Apply the solution with a needle under a microscope. The disadvantage of the method is the effect on the viability of the embryo. In order not to harm the embryo, after the procedure it is thoroughly washed.
Auxiliary laser hatching. It is performed with a very thin laser beam in a non-contact way. It is laser hatching of embryos that is considered the most accurate and safe for the fetus. The effect of using a laser is much higher than that of other types. Laser assisted hatching has only one drawback - the equipment for its implementation is very expensive.
Piezo technique. A modern method based on the impact on the embryo with a piezoelectric micromanipulator. This allows you to thin the walls of the shell and help the fertilized egg to get out and attach to the walls of the uterus.
The embryologist, taking into account all the indications of the patient who came for in vitro fertilization, will decide on the need for assisted hatching. In some cases, this is the only way to help the egg, after fertilization and passing through the fallopian tube, free itself from the membrane and attach to the walls of the uterus.