Many pregnant women are faced with a doctor's diagnosis such as the threat of termination of pregnancy. Quite often this term can be heard in the early stages. Even before conception, during pregnancy planning, a representative of the fair sex must prevent the threat of miscarriage from occurring in the future.
If you had to deal with this diagnosis already during pregnancy, then you should not worry or panic, since this condition can be successfully dealt with.
The possibility of miscarriage is a scary situation that any pregnant woman can face. According to statistics, spontaneous abortion occurs in 10-20% of cases, and more than half of them occur in the early stages (from the moment of conception to 22-23 weeks). Other women face the risk of premature birth between 22-23 and 37 weeks.
Threat of early pregnancy loss is more dangerous, since if a woman does not seek help in a timely manner, the fetus may not be saved. In cases of premature birth, children survive thanks to modern technology and advances in medicine. That is why doctors, when detecting a threat of miscarriage, strive to prolong the pregnancy (increase the period of intrauterine development of the child).
Reasons for the threat of miscarriage in the early stages
Every woman should know about the factors that can cause a miscarriage. The reasons for the threat of miscarriage may be different. Some of them are genetic. Violations of the chromosomal and gene structure of the fetus are accompanied by malformations.
Pregnancy can be interrupted from conception to , if the violations are incompatible with life. With pathologies compatible with life (for example, Patau, Edwards, Down syndromes), a miscarriage may not occur, but the threat of termination of pregnancy will accompany the woman throughout the entire pregnancy.
A representative of the fair sex in this position is subject to various infections. They do not pass without a trace. Even the most seemingly harmless diseases can lead to tragic consequences. Miscarriages are very common due to infections. Only competent and timely treatment of diseases can prevent fetal death.
Pregnancy may be terminated by immunological reasons. For example, some women with a negative Rh factor who are carrying a child with a positive Rh factor may experience Rhesus conflict: The mother’s immune system may react inadequately to the fetus, since it is half a foreign body. However, this only happens to 30% of women. In the remaining 70%, the immune system does not respond to the fact that the fetus has the opposite Rh factor.
Another reason for the threat of miscarriage in the early stages is hormonal imbalance. It is known that pregnancy is supported by certain hormones produced in the female body. Deviations from the norm can negatively affect the condition of the fair sex.
For example, one of the reasons for a miscarriage may be hyperprolactinemia when there is an increased level of prolactin. In the early stages, this hormone inhibits the production of the main hormone that supports pregnancy - progesterone. If its level decreases, a miscarriage may occur.
Another hormonal reason for the threat of interruption of the “interesting situation” is hyperandrogenism, characterized by an increase in the level of production of male sex hormones in a woman’s body.
Irregularities at work thyroid gland- another reason, the consequence of which may be a miscarriage. Thyroid hormones are very important for the normal course of pregnancy. A risk to pregnancy can occur with both hyper- and hypofunction of the thyroid gland.
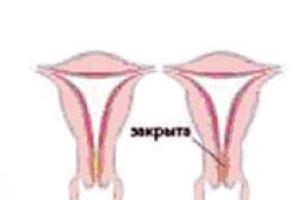
The threat of miscarriage in the early stages is also pathological cervical condition and the isthmus of the uterus, called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. They are not able to hold an expanding fetus. As a rule, a miscarriage with this condition occurs at 12-18 weeks of pregnancy. With timely diagnosis, disastrous consequences can be avoided, since the pathology can be corrected.
Anomalies in the structure of the genital organs can lead to miscarriage. Disturbances in the anatomical structure of the uterus (bicornuate uterus, the presence of a septum in its cavity) are often combined with a lack of sex hormones. All this is the reason for the inferiority of the muscular layer of the organ in which the fetus should be born.
The development of pregnancy can be affected by various injuries. Concussions are especially dangerous: past injuries that disrupted the brain’s blood circulation can be recalled after conception.

Thanks to timely diagnosis of any abnormalities, the threat of miscarriage can be prevented. At the slightest symptoms of this condition, you should contact a medical facility for help.
Symptoms of threatened miscarriage in the early stages
One of the signs of an impending miscarriage is nagging pain lower abdomen, lower back pain. At the beginning of pregnancy, discomfort in the lateral parts of the abdomen may make itself felt. They are not related to miscarriage, since their occurrence is associated with changes in the ligaments of the uterus.
Blood, secreted from the genitals, may indicate the presence of a threat of termination of pregnancy in the early stages. Unfortunately, some women perceive it as their period. This point of view is absolutely wrong. There cannot be menstruation during pregnancy.
Even a small amount of bloody discharge indicates an unfavorable course of pregnancy. In the early stages, the cause of their occurrence lies in the detachment of the fertilized egg.
Hypertonicity of the uterus- another symptom of a threatened abortion in the early stages. Increased tone in the 1st trimester can be observed on the back or front wall of the uterus. The woman does not feel it, but this is determined by ultrasound. This condition may be the result of psychological stress. For such a woman, the doctor prescribes the necessary antispasmodics and recommends repeating an ultrasound scan after 10 days.
In a condition called total hypertonicity, the uterus becomes “stony” and painful sensations occur. For doctors, this is a sign of a threat of miscarriage. The sooner it is diagnosed, the easier it will be to maintain the pregnancy, so it is very important to monitor the condition of your body and, if you suspect it, you should immediately consult a doctor for help.
Possible treatment for threatened miscarriage
If the condition of a pregnant woman does not cause serious concern, then the specialist may prescribe ambulatory treatment. The pregnant woman will have to maintain psychological as well as physical rest. Some women are prescribed sedatives if necessary, because they are very anxious and worried that the baby they carry under their hearts is in danger.
If there is a strong threat of miscarriage, the woman is hospitalized in gynecological department. She finds herself isolated from her relatives, friends, and work. For many this is beneficial. This makes it easier to concentrate on your baby and push all problems and worries into the background.
A woman staying in a medical facility feels especially protected, because if necessary, she will quickly receive qualified assistance.

Specific treatment for threatened miscarriage in the early stages depends on the cause of its occurrence. For example, if there is a possibility that a miscarriage may occur due to hormonal imbalance, then certain hormones are prescribed to promote the normal course of pregnancy.
If an ultrasound and examination reveals isthmic-cervical insufficiency, then doctors put sutures on the cervix, thanks to which the fertilized egg will not be “released” from the organ. The operation is performed under general anesthesia using drugs that relax the uterus.
When immunological factors are identified, treatment of threatened miscarriage in the early stages is aimed at suppressing the production of antibodies.
If a woman has uterine tone, then medications are prescribed to relieve spasm of the uterine muscles. Most often, such drugs are administered using a dropper.
In the presence of infectious, chronic, inflammatory diseases, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Prevention of threatened miscarriage in the early stages
In any situation and for any illness, it is much easier to take preventive measures than to find yourself in a situation in the future in which medical workers can no longer help.
Any woman needs in advance plan a pregnancy. This preparatory period is of great importance. During planning, various examinations are carried out and tests are taken. Thanks to all this, you can find out if your partners have any problems or diseases that could cause a risk of miscarriage after conception.
Don't forget that planning can take a long time. By starting to prepare for conception early, you can significantly improve your health.
A pregnant woman should regularly visit a doctor who monitors her condition and the development of the fetus. The main goal of monitoring pregnancy is to identify possible risks and pathologies as early as possible. Only timely diagnosis can have an impact on the course of pregnancy, child development and childbirth.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to protect your body from stress, overwork, because all this weakens the immune system. This can lead to the appearance of various diseases, which may result in the threat of miscarriage in the early stages.
Representatives of the fair sex in position, leading healthy lifestyle and those wishing to engage in physical exercise should consult a doctor about this. He will help determine whether a woman has any contraindications for exercise, and will recommend specific exercises that will not harm either the expectant mother or her baby, but will only benefit both.
If there are any infectious, inflammatory diseases There is no need to self-medicate and take medications that the doctor did not prescribe. In general, during pregnancy you should protect yourself from illnesses, since taking medications during this important period for any woman is undesirable. If, nevertheless, it was not possible to avoid infections, then you need to strictly follow the treatment prescribed by the doctor and follow all his recommendations. Only an experienced specialist can prescribe medications that will not harm the fetus.

A pregnant woman with or without a threat to her position shouldn't worry. It is worth reminding yourself as often as possible that at the moment the most amazing and wonderful days are going on in life. You need to enjoy this period. You should pay special attention to your diet, sleep patterns, walks, and work.
A woman must learn to relax, discard bad thoughts, and avoid negativity. This is the only way to achieve the birth of a healthy, nice and strong baby.
Thus, most life situations in which the threat of miscarriage makes itself felt can be safely avoided. It is very important to plan ahead for your pregnancy. Examinations will help identify reasons that may lead to the loss of a child in the future.
The dream of bearing a healthy child, unfortunately, can be overshadowed by a condition that is designated by the medical term “threatened miscarriage.” Experts perceive it as a guide to action - procedures and prescriptions that will stop fetal rejection. It is important that a woman finds the strength to fight for the life of her child.
What is a threatened miscarriage?
A miscarriage that occurs in the first 4 obstetric weeks is called a preclinical abortion. It occurs even before implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterus and is caused by biochemical processes after the body mistakes the fertilized egg for a foreign body. Pregnancy at such a time is not recognized, and the release of the embryo is taken for the next menstruation. The fact that conception has occurred can only be indicated by a laboratory test for hCG if it is done at 1–2 weeks, but in practice this happens very rarely.

Spontaneous abortion can occur starting from the 5th obstetric week. The fetus is considered non-viable until the 20–22nd week, which is why in the early stages we are talking about miscarriage, after 22 weeks we are talking about premature birth, during which there is still a chance to save the child’s life.
Miscarriage can be caused by increased uterine tone. As a result of strong muscle contractions, the cervix opens completely or partially, and the fertilized egg (or fetus) comes out of its cavity.
The threat of miscarriage is the initial stage of the pathology, when risks are identified that, without the intervention of doctors, can lead to termination of pregnancy. At this stage, measures are taken to stop the development of dangerous symptoms.
At the same time, a diagnosis is carried out and a comprehensive treatment is selected that will eliminate the risk of miscarriage or at least increase the duration of gestation.
The concept of “threatened miscarriage” is used in cases where uterine hypertonicity is established, there is pain and bleeding, but the rejection process is not observed. This condition is amenable to therapy aimed at maintaining pregnancy.
Reasons for threatened miscarriage

Some threatening preconditions that increase the likelihood of spontaneous abortion can be established during the collection of the pregnant woman's medical history. Past miscarriages, abortions, births by cesarean section, chronic diseases, anatomical features and other facts are taken into account, but do not serve as a sufficient basis for establishing a threat.
Certain symptoms that precede fetal rejection may be indications for medical and surgical intervention. For adequate treatment, it is necessary to find out exactly what factors are involved in creating the threat of miscarriage. They are divided into 2 groups:
- endogenous, associated with the internal processes of embryo development;
- exogenous, associated with the external conditions in which pregnancy occurs.
Endogenous causes
This group includes features of the chromosomal and gene structure of the fetus, immune and hormonal disruptions, and anomalies in the structure of the reproductive organs. More than half of spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy occur due to genetic mutations of the fetus.
Abnormal development of the embryo is provoked by a one-time failure or hereditary factors, as a result of which a complex natural mechanism is triggered, triggering the termination of an inferior pregnancy. Nature recognizes and stops the development of a non-viable fetus at an early stage.
It is impossible to prevent such a miscarriage by medical intervention. This tragic loss is not a death sentence; doctors help determine the cause and reduce the risk of repeat miscarriage in the future.

Hormones are stimulants of body restructuring, and the slightest disruption in their production can lead to complications at all stages of pregnancy. The threat of interruption occurs when the level of hCG is insufficient, which triggers the process of restructuring the endocrine system.
Progesterone, which is produced in the corpus luteum, then in the placenta, ensures the successful consolidation of the fetus. Its deficiency triggers the process of rejection. The same danger is posed by a decrease in the production of estradiol, the concentration of which affects the condition of the placenta. The cause of hormonal imbalance can be the increased production of androgens, which suppress the secretion of female hormones. To maintain pregnancy, the full functionality of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland is also important.
Congenital pathologies in the structure of the uterus - one-horned, two-horned or saddle-shaped uterus, fusion or underdevelopment of the uterus - lead to impaired reproductive function. Acquired pathologies - neoplasms, tissue dysfunction resulting from curettage, abortion and cesarean section also create a risk of termination of pregnancy for up to 12 weeks. An established embryo does not receive enough nutrients and does not have space for growth; an anomaly in the development of the placenta occurs. Women who become pregnant through IVF are at increased risk.

Miscarriage can be caused by isthmic-cervical insufficiency, in which the relaxed muscle ring of the cervix cannot withstand the load and begins to open prematurely, creating a risk of fetal loss. Pathology occurs due to tissue injury or hormonal dysfunction.
Serious illness of a woman can also trigger the natural mechanism of termination, since the developing pregnancy poses a threat to her life. In addition, pregnancy is incompatible with medications that support a sick body. They cause abnormal development of the fetus and can lead to an abortifacient effect.
Increased blood clotting, as well as a predisposition to bleeding, pose a risk of miscarriage. A separate case is the Rh conflict during repeated pregnancies, when the mother’s body with a negative Rh factor perceives a fetus with a positive Rh factor as a foreign element and rejects it.
Exogenous causes

External factors that provoke miscarriage include:
- injuries and physical strain: falls, impacts, heavy lifting lead to mechanical injury incompatible with pregnancy;
- infections and viruses: sexually transmitted diseases, rubella, tonsillitis, hepatitis and other infections that are accompanied by inflammatory processes can provoke spontaneous abortion;
- Physiological stress, which occurs due to the inability to adapt to emotional turmoil, severe physical pain or sudden changes in the environment, can also cause the onset of the process of fetal rejection;
- poisoning of the body with pharmacological drugs and toxins that have an abortifacient effect occurs when taking hormone-containing drugs, analgesics, antibiotics, narcotics and smoking.
Symptoms of threatened miscarriage
Tension and pain in the lower abdomen during the normal course of pregnancy are associated with an increasing load on the ligamentous apparatus of the abdominal cavity. If the pain is caused by a threat of miscarriage, it will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nagging and sharp pains radiating to the lower abdomen and lower back;
- attacks of pain that do not subside when changing position and begin at rest;
- brown or bloody discharge;
- convulsive tightening pain and hardening of the abdomen, lasting more than 3 minutes and occurring more often 4-6 times a day.

An alarming sign is uterine bleeding of any intensity, which indicates placental abruption. It can occur without pain, but even in this case it poses a risk to the health of the mother and fetus. Yellowish or greenish discharge with an unpleasant odor is also a reason to visit a gynecologist.
Bleeding, discharge and pain may decrease or stop. The need to see a doctor remains, since a miscarriage can occur unexpectedly and in a short time.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis is carried out in order to ascertain the threat and find the reasons that provoke a miscarriage. If there are alarming symptoms, a gynecological examination of the cervix is performed to confirm or refute the danger.
Ultrasound examination of the position and condition of the fetus, placenta, and uterine walls helps indirectly confirm the likelihood of hypertonicity and abruption. Identification of the causes of this condition occurs as a result of hormone tests, laboratory tests to determine viral and bacterial infections, and checking blood clotting indicators. For early detection of hormonal imbalance, a smear of mucous substances is taken from the walls of the vagina.

How to maintain pregnancy: treatment methods
Complex therapy for maintaining pregnancy is prescribed on an individual basis (for more details, see the article: therapy for maintaining pregnancy in the early stages). The advisability of using medications and surgery depends on the reasons that created the threat of miscarriage.
In any case, measures are taken to reduce uterine hypertonicity, relieve psychological stress and limit the physical activity of the pregnant woman. Depending on the degree of threat, treatment is carried out in a hospital or at home.
Medicines
Antispasmodics are used to provide first aid for symptoms of miscarriage. Tablets "No-Shpa" and "Papaverine" in case of threat of miscarriage are traditional means for quickly reducing contractile function and allow you to gain time for diagnostic procedures. No-Shpa and Papaverine are considered traditional remedies for relieving pain during pregnancy, but their long-term use is possible only as prescribed by a doctor (we recommend reading: Papaverine suppositories for relieving pain during pregnancy).

To relieve tension in the smooth muscles of the uterus in the 2nd trimester, tocolysis with a solution of magnesium sulfate, which is known as Magnesia, is used. The drug is administered by intravenous injection or through a drip. Magnesia is considered safe for the fetus after the 1st trimester, can be prescribed in dynamic dosages and is used for a long period intermittently as the main remedy against uterine hypertonicity. Magnesia can cause adverse reactions, which serve as sufficient grounds for discontinuation and search for alternative remedies.
The calming effect can be provided by valerian or desert extracts. Magne B6 is a drug with a sedative effect that reduces anxiety.
After laboratory tests, hormonal therapy may be prescribed. If progesterone deficiency is established, drugs containing it are used.
To stop uterine bleeding in a hospital setting, injections of tranexamic acid are used. If an inflammatory process is diagnosed, Indomethacin suppositories, gentle antibiotics, and immune drugs are prescribed.
General restorative therapy with vitamins and bioactive supplements is prescribed in combination with drug treatment to reduce the harmful effects of drugs or replenish the deficiency determined by tests. If the cervix opens early, surgical intervention is necessary - suturing, after which the woman is prescribed bed rest. Suppositories with papaverine, which can be taken in the second and third trimesters, are used to relieve gastrointestinal spasms and lower blood pressure.
Folk remedies

Treatment with herbal tinctures can have an anti-inflammatory effect, relieve swelling, reduce the likelihood of bleeding, strengthen the immune system, but the use of herbal medicine must be agreed with a doctor. Many natural remedies have contraindications, compatibility requirements and side effects. In folk medicine books there are special recipes for herbal remedies recommended during pregnancy. They use licorice roots, elecampane, viburnum bark, yarrow, nettle, and calendula.
Behavior and lifestyle of a pregnant woman with a threat of miscarriage
The threat of miscarriage increases a woman’s responsibility for the child’s life, which can lead to panic, increased anxiety, insomnia, and emotional instability. Hospitalization, bed rest, or simply limited movement become an additional stress factor. It is important for a pregnant woman to adequately assess her condition and avoid breakdowns. Trust in the doctor and a positive attitude play an important role, since a state of rest is one of the conditions for maintaining pregnancy.
Strict adherence to recommendations regarding restriction of physical activity, bed rest, and prohibition of sexual intercourse is critical for the effectiveness of therapy. In addition, a pregnant woman will have to adapt her diet to a sedentary lifestyle, do all prescribed procedures on time, and be attentive to the prevention of infections and the safety of the environment.

Prevention measures
Reliable prevention of the threat of miscarriage is planning a pregnancy and undergoing a special medical examination, based on the results of which preparatory therapy can be prescribed. Many reasons that lead to termination of pregnancy can be eliminated in advance. This is especially true for chronic diseases and infections that need to be treated before conception.
Research into the functioning of the endocrine system, the functionality of the reproductive organs, and genetic inheritance requires preventive measures that will help avoid complications. Early cessation of bad habits is another step necessary to reduce risks.
One of the greatest and long-awaited joys for a woman is, of course, the joy of motherhood. Having learned about her pregnancy (according to the results of a test or confirmation from a doctor), a woman already casually looks at the display cases with children's things and toys, plans how and where she will give birth, comes up with a name for the future baby, etc. True, no one around has yet notices that you are pregnant, since the baby inside you is very tiny and is just beginning its difficult path of development and growth.
Unfortunately, your happiness may be darkened ‒ medical statistics states that a quarter of early pregnancies end in miscarriage. At this time, a woman may not yet be aware of the changes in her body. Then it is a little easier for her to cope with the pain of loss.
How to avoid early miscarriage? To do this, expectant mothers need to know what can trigger a miscarriage, what symptoms and signs it is accompanied by, how to prevent them and whether they can be avoided.
This problem in medicine is considered quite serious, because it is encountered often, and in most cases the process is almost impossible to stop. If a miscarriage or spontaneous termination of pregnancy occurs at the very beginning, then the woman may not even understand what happened.
Without realizing her situation, the woman simply thinks that the menstrual cycle has gone wrong or there has been a delay (usually a week or two). Then some feel minor abdominal pain, and menstruation begins, which, however, can be much heavier than usual. Not all women deal with this, but only those who are frightened by the release of a blood clot, similar to a burst bubble.
Nevertheless, it's worth going to the doctor, even if nothing else bothers you. They will do an examination to see if it was indeed an early miscarriage, and will also check whether additional cleaning is needed after this.
If a woman knows about her pregnancy, then she needs to be very attentive to any manifestations of pain or discomfort in the abdomen and back. The slightest spotting with an admixture of blood or tissue clots is already dangerous. Sometimes pregnancy can still be maintained, so you should contact your doctor immediately.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy occurs before 12 weeks, which is classified as an early miscarriage. If it happens before 22 weeks, it will already be late. Unfortunately, this also happens for a number of reasons. Then doctors define this threat as premature birth, and with prompt and timely intervention they can save the premature baby.
Causes of threatened miscarriage in early pregnancy
 Why does early miscarriage occur? Sometimes a woman faces this problem several times in a row. Doctors call this recurrent miscarriage.
Why does early miscarriage occur? Sometimes a woman faces this problem several times in a row. Doctors call this recurrent miscarriage.
The cause of spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages is very difficult to determine; this will require a comprehensive detailed examination, many different tests and appropriate treatment.
But it may also happen that even this will not help, that is, the termination of pregnancy will be influenced by factors that simply cannot be predicted or prevented.
The main reasons that cause or provoke miscarriage include a number of socio-biological and medical factors. The first group is purely personal and subjective reasons:
- unfavourable conditions(place of work in hazardous production, radiation, exposure to environmental toxins, difficult psycho-emotional background and microclimate in the family, etc.);
- Unhealthy Lifestyle and bad habits (if you are, then you should quit smoking, don’t drink alcohol, give up strict diets, excessive coffee consumption, adjust your diet and daily routine);
- woman's age is also often one of the causes of miscarriage;
- stressful situations, nervous shocks or strong emotions are a serious threat to a little life. A woman should protect herself from all this, but under no circumstances take sedatives, so as not to harm the baby even more. It is better to consult a doctor to find the right way out if stress cannot be avoided;
- do not ignore the danger that all kinds of physical exercise. Avoid heavy physical work and do not lift heavy objects (even bags with groceries that weigh more than 5 kg are taboo for you). You will also have to approach sports with caution. Some types, especially extreme ones, cannot be combined with pregnancy. Be careful with hot baths, baths or saunas;
- if it happened to you accident(unforeseen emergency, car accident, etc.) so you are seriously injured or injured, your body may not be able to cope with maintaining the pregnancy. Even a minor fall due to negligence (uncomfortable shoes, ice, etc.) is dangerous.
Medical reasons or women's health problems
- Doctors say that early miscarriage is most often caused by genetic disorders or abnormalities in the fetus. A woman may suffer from a hereditary form of the pathology, although there are also isolated mutations that lead to the death of the embryo. This is influenced by a whole range of different factors: radiation, viruses, unfavorable environmental conditions, etc. It is no longer possible to control or stop this process. Thus, nature itself produces a kind of control, saving you from non-viable offspring. However, doctors recommend that couples who want to conceive a healthy child seek advice from a geneticist, and also carefully prepare for the upcoming pregnancy.
- Very often, the cause of spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages is hormonal disorders in a woman's body. If you detect the problem in time and seek help from a doctor, this threat can be eliminated. The most common complaints are about a deficiency, although there are also cases of increased levels of male hormones. Problems with the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, which prevent the organs from functioning correctly and fully, also cause miscarriages. Usually in such cases, hormonal therapy or appropriate treatment is prescribed. It is better to check the condition of your body before pregnancy.
- Any pathology of the immune system threatens termination of pregnancy. The most common manifestation is considered to be a complication in the form of Rh conflict. This means that your body is fighting an embryo that is foreign to it and rejecting it, because its blood Rh factor is negative, and the one taken from the father is positive. If such a possibility exists, doctors recommend prophylaxis with immunomodulators.
- Very dangerous for any kind of pregnancy infections. This includes all sexually transmitted diseases: herpetic and cytomegalovirus infections, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, syphilis, trichomoniasis and others. Due to the fact that the membranes are affected by viruses and pathogenic bacteria, the fetus itself can be infected, which leads to miscarriage.
- Also a serious risk for the baby are inflammatory diseases internal organs and even general infectious diseases: viral hepatitis, rubella, influenza or sore throat with complications and fever, pneumonia and others. When planning a pregnancy, pay close attention to your health in order to identify and eliminate any possible dangers.
- It is worth calling a huge stress for the female body abortion. If previous pregnancies were interrupted artificially, then there is a huge risk of complications that lead to miscarriage or even secondary infertility. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have had an abortion before.
- The first trimester of pregnancy practically excludes the intake of any medicines, medications and even herbs. All this often poses a great threat to the life of the fetus and affects its development. Never self-medicate, because even simple parsley in the form of a seasoning can lead to. Always consult your gynecologist and read the instructions carefully.
They also cause miscarriage individual characteristics of the body women. So, if she suffers from congenital anomalies of the structure of the uterus, isthmic-cervical insufficiency, oncological diseases of the genital organs or other pathologies, then often the pregnancy simply cannot be maintained.
Threatened miscarriage in the early stages: signs and symptoms
 How to recognize an early miscarriage and what are the symptoms?
How to recognize an early miscarriage and what are the symptoms?
There are several main stages of spontaneous abortion, since it does not happen all at once. Each of these stages is characterized by its own symptoms due to the threat of miscarriage in the early stages, and sometimes this can be stopped or prevented, if you seek treatment from a doctor in time.
So, the first signs of early miscarriage that should alert you any manifestations of pain or pain in the back and abdominal area, which is accompanied by brown or red discharge. Sound the alarm even if a few drops of blood appear from the vagina, because this may already indicate an early miscarriage. Also pay attention to your condition: have the main signs of pregnancy disappeared?
Don't miss it routine visits to the doctor, passing mandatory tests or necessary examinations. This way you can rule out any pathologies in the development of your baby and be confident that the pregnancy is going well.
Main stages of miscarriage
- Threat or risk spontaneous abortion. This condition happens very often, which is why some women are forced to remain in bed for almost the entire 9 months. It is characterized by the above-mentioned cramping pains and bleeding, sometimes even very copious ones. You can also note increased uterine tone.
- The second stage is more serious - it is classified as incipient miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. The fertilized egg has already partially detached from the walls of the uterus, so the symptoms of spontaneous miscarriage in the early stages will be pronounced. But doctors still consider this stage to be reversible, that is, with prompt and qualified intervention, they can save your child’s life.
- With the so-called "miscarriage in progress" The pregnancy cannot be saved. At this stage, the woman feels severe and sharp pain, and heavy bleeding occurs almost immediately. The fertilized egg has already died, and the cervix is open, so it can come out all at once or in parts, which will be considered an incomplete miscarriage.
- The last stage is completed spontaneous abortion. The uterus, having expelled the dead fertilized egg, contracts and returns to its previous size.
Treatment and consequences after miscarriage in early pregnancy
What to do after a miscarriage in early pregnancy? If it did happen that the pregnancy could not be maintained and you lost the child, then you need to undergo therapy, which is mandatory after a miscarriage. The doctor should send you to body examination to determine the reason that caused the miscarriage (if this has not been done previously).
 You definitely need to check whether the fertilized egg has completely left the walls of the uterus, since if the abortion is incomplete or not completed, you will need curettage. There will also be antibiotics were prescribed, which will help cope with a possible infection, and hormonal contraceptives. This stabilizes your hormonal levels.
You definitely need to check whether the fertilized egg has completely left the walls of the uterus, since if the abortion is incomplete or not completed, you will need curettage. There will also be antibiotics were prescribed, which will help cope with a possible infection, and hormonal contraceptives. This stabilizes your hormonal levels.
In addition to the physical stress on the body, miscarriage is very serious psychological and emotional test for any woman. The pain of loss can develop into severe, protracted depression, especially if the pregnancy was long-awaited and desired. Don’t isolate yourself during this difficult time, try to trust your spouse, parents, and loved ones so that they will support you and help you get through the grief. Allow yourself to be sad and cry, you can even seek help from a psychologist if you are unable to cope with your feelings.
You should not be afraid of the same failures in the future and despair. Just be more responsible about your next one early on. Remember that the body is still restoration required, so don’t rush to become a mother again for at least six months. During this time, you can get rid of existing problems, drink alcohol, and undergo complex therapy prescribed by the doctor.
The correct psychological attitude and only positive thoughts that everything will be fine with you, and after a certain period of time you will take your long-awaited baby in your arms is also very important.
 If you find out that you are carrying a small life inside you, then you need to minimize as much as possible the potential risks that could lead to miscarriages. Follow simple rules: adjust your diet, give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle, don’t overwork, be extremely careful, avoid stress and nervous shock.
If you find out that you are carrying a small life inside you, then you need to minimize as much as possible the potential risks that could lead to miscarriages. Follow simple rules: adjust your diet, give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle, don’t overwork, be extremely careful, avoid stress and nervous shock.
Be sure to stand on registration in antenatal clinic. The doctor will help identify illnesses or problems that you did not even know about, but that may pose a threat to your baby. Timely treatment or prevention will help prevent the threat of miscarriage. Follow all the recommendations your gynecologist gives you.
At the slightest sign of danger go to the hospital immediately. In most cases, pregnancy can still be maintained. If you have experienced the loss of a child, do not despair and do not be alone with your pain.
Video about miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy
We invite you to watch one of the episodes of the pregnancy video guide, where they will tell you about such a problem as miscarriage, what could be the cause and how to cope with the loss.
Please share in the comments, have you encountered a similar problem: what helped you prevent the threat, what symptoms and signs were it accompanied by, did you prepare for conception in advance, what kind of therapy did you undergo?
According to statistics, out of 100 pregnancies, 15–20 end in miscarriages. Most often this happens when the woman does not yet know about her situation. But if the expectant mother is already aware that conception has occurred, then a miscarriage becomes a terrible loss for her. Therefore, information regarding miscarriage will be useful both to those who are at the planning stage and to women already expecting a baby. Knowing the causes and symptoms of spontaneous abortion in the early stages, you can prevent the threat of losing a child, as well as avoid unpleasant consequences.
What is spontaneous abortion
Miscarriage (spontaneous or spontaneous abortion) is the rejection of the fetus by the mother’s body for reasons beyond her control for up to 28 weeks.
Statistics of pregnancy rates among women in Russia
There are three types of spontaneous abortion (depending on the period at which the miscarriage occurred).
- Termination of biochemical pregnancy (up to 3 weeks). For unknown reasons, the embryo detaches from the walls of the uterus and comes out along with blood clots. Bleeding at these times is in most cases perceived as the beginning of menstruation, since the woman does not yet know about her pregnancy.
- Early miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion. Termination of pregnancy occurs before the third trimester.
- Premature birth, or late miscarriage. The reasons may be various pathologies of the fetus, circulatory disorders, gestosis in the mother, etc. In most cases, with a miscarriage in the later stages, the child can be saved.
In each period of pregnancy, there are periods during which the threat of miscarriage is most likely. The highest risk of losing a baby occurs in the first month after conception, especially from 14 to 21 days.
In addition, you need to be extremely careful during the following periods: 8–12, 16–20, 28–32 weeks. During these periods, a woman should rest more, avoid stress, listen to her feelings and visit a doctor in a timely manner.
If signs of an incipient miscarriage are detected, a woman should immediately seek qualified medical help. Timely measures taken increase the chances of maintaining the pregnancy and a successful delivery on time.
Threat of miscarriage - how to maintain pregnancy (video)
Types
Miscarriages are divided into several types:
- Inevitable (incomplete). He is accompanied by severe pain, covering the lower back and lower abdomen. Accompanied by cervical dilatation and uterine bleeding. A miscarriage is considered inevitable when a rupture of the membranes forms and the internal os of the uterus opens. Continuous pain and discharge are signs of an incomplete miscarriage.
- Complete - spontaneous termination of pregnancy, in which the embryo or fetus is completely expelled from the uterine cavity. After complete cleansing of the organs, pain, spasms and bleeding disappear. Surgery is rarely required.
- Failed miscarriage or frozen pregnancy. The dead fetus remains in the uterus; at first, no symptoms are observed. Most often it is diagnosed at a routine appointment with a gynecologist or by ultrasound. Surgery is mandatory.
- Repeated miscarriage. Happens in about one in a hundred couples. When a woman has three pregnancies in a row end in arbitrary termination in the early stages.
- Anembryony. Fertilization and attachment of the egg occurs, upon examination, an enlargement of the uterus is observed, a fertilized egg is formed, and other symptoms of pregnancy are also present. But the fetus either does not develop or dies at the initial stage.
- Chorioadenoma. Develops due to genetic disorders. In place of the amniotic sac, just a piece of tissue is formed, which gradually increases in size.
If these conditions are diagnosed early, the woman must undergo an abortion for medical reasons.
Features in the early stages
In most cases, complete or incomplete miscarriages occur in the early stages of pregnancy.
- With a complete miscarriage, the uterus rejects the fetus completely, along with the waters and amniotic sac.
- In the case of an incomplete miscarriage, most often only the embryo is rejected, and the amniotic membranes remain in the uterine cavity. The embryo can come out either completely or partially.
To avoid the serious consequences of an incomplete miscarriage, the woman is cleaned and also prescribed hemostatic, hormonal, antibacterial medications that cause uterine contractions.
After cleaning, it is imperative to perform an ultrasound to make sure that there are no blood clots or fetal tissue left, and that the uterine lining is being restored.
Causes
Most often, the causes of miscarriage are genetic abnormalities and fetal malformations that are incompatible with life. This is why some doctors prefer not to continue pregnancy until 12 weeks, arguing that this is due to natural selection. In some cases, abortion is offered for medical reasons.
If a woman is hospitalized for preservation, then in most cases doctors are able to prevent a miscarriage. In this case, if possible, a complete examination of the fetus is carried out for the presence of genetic abnormalities. And only then is a decision made on further tactics for managing the pregnancy or a referral to terminate it is issued.
The main causes of early miscarriage:
- Genetic defects:
- anatomical (congenital and acquired malformations);
- infectious (chronic endometritis);
- genetic (structural or quantitative change in chromosomes);
- endocrine;
- thrombophilic;
- immunological (autoimmune and alloimmune).
- Violation of hormone levels and thyroid function.
- Diseases of the reproductive system, sexually transmitted infections.
- Viral and infectious diseases (flu, sore throat, rubella, chickenpox, toxoplasmosis).
- Impaired blood flow between mother and child;
- Severe pathologies of the internal organs of the fetus.
- Bad habits of the mother (smoking, alcohol, drugs).
- Stress, nervous tension.
- Physical activity, heavy lifting, injuries.
- History of abortion, scars on the uterus and abdominal cavity.
- Taking medications contraindicated during pregnancy.
- X-ray radiation.
The causes of early fetal rejection can also be attributed to a later period, although in the second and third trimesters, miscarriage is most often provoked by inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity or placenta.
Signs in the early stages
The following symptoms indicate a threat of miscarriage:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- vaginal bleeding (scarlet or brown discharge, spotting or heavy);
- convulsions.
In the early stages, it is not always known about pregnancy, so the symptoms of a miscarriage can easily be mistaken for the beginning of a new menstruation. It is worth noting that there are secondary signs of spontaneous abortion that distinguish it from menstrual periods, in particular:
- vomiting and frequent loose stools;
- pain in the form of spasms;
- weight loss;
- bleeding alternating with mucus;
- aching pain in the lumbar region.
If you know you are pregnant and even minor bleeding begins, you should urgently seek medical help.
There is such a thing as a frozen pregnancy, or a failed miscarriage. This is the cessation of fetal development and its death for up to 28 weeks. Signs of this condition:
- absence of toxicosis;
- decrease in basal temperature;
- weakness.
In addition, the symptoms of a miscarriage may vary depending on the stage of its progress.
Symptoms depending on the stage of miscarriage (table)
| Stage | Clinical picture |
| State of threatened miscarriage | This stage is accompanied by aching pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. In some cases, spotting and spotting appears. |
During the second stage of miscarriage, the pain becomes cramping, there is general weakness and dizziness. With every movement, the bleeding increases, and there are clots in the discharge. |
|
| Miscarriage in progress (or in progress) | Symptoms of miscarriage are a sharp pain that spreads throughout the abdomen and lower back, significant blood loss and the release of the fertilized egg from the uterus. In some cases, a woman may see a small gray bubble in the discharge; most often this happens if the fetus died a few days before the development of the main symptoms. |
| Completed miscarriage (completed abortion) | The bleeding gradually becomes less intense, but spotting may continue for several days. |
Timely diagnosis of the threat of miscarriage and the onset of spontaneous abortion (first and second stages) with adequate treatment leave a chance of saving the child. The next stages are irreversible and lead to termination of pregnancy.
Stages of spontaneous miscarriage (gallery)
 Bleeding after spontaneous abortion can last from 4 to 10 days
Bleeding after spontaneous abortion can last from 4 to 10 days  Some time later, the fertilized egg and placenta are expelled from the uterus
Some time later, the fertilized egg and placenta are expelled from the uterus  Clinical picture of a miscarriage: bleeding, accompanied by spasm and pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lumbar region
Clinical picture of a miscarriage: bleeding, accompanied by spasm and pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lumbar region
Spontaneous abortion or menstruation?
It is possible to determine that a pregnancy has been terminated and that another menstruation has not occurred by monitoring the level of hCG in the blood and measuring basal body temperature.
Basal temperature is the lowest body temperature, which is measured immediately after sleep, without getting out of bed.

Prevention
Even a completely healthy woman is not immune from spontaneous miscarriage. It is not always possible to detect genetic mutations, hereditary or chronic diseases, which often manifest themselves during pregnancy.
But you can follow simple rules that will allow you to conceive a healthy child and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. Among them:
- moderate and healthy eating, weight control;
- complete cessation of alcohol and cigarettes;
- taking multivitamins;
- elimination of stress and overload;
- frequent and long walks in the fresh air;
- gymnastics or physical education classes;
- complete rest;
- routine examinations with a doctor.
After an early miscarriage, a woman should undergo a full examination, treatment, and only with the permission of a doctor begin planning a new pregnancy.
According to statistics, 2 out of 10 pregnancies end in spontaneous miscarriage. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor your well-being while carrying a child. If specific symptoms occur, seek medical help immediately. Timely diagnosis and treatment will preserve your pregnancy and minimize the risks of its termination.
Why is there a threat of miscarriage in the early stages and what to do to avoid losing the desired pregnancy? More than one pregnant woman asks this question. What is generally understood by the threat of miscarriage or the threat of termination of pregnancy?
In medicine, this diagnosis is called threatened miscarriage or threatened abortion and is manifested by bleeding from the genital tract and (or) increasing pain in the lower abdomen.
Threatened miscarriage: symptoms.
So, the threat of miscarriage has two main symptoms: spotting and abdominal pain. However, these symptoms do not necessarily indicate a threat of termination of pregnancy.
Many women experience bloody discharge in the first trimester, which may be due to implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall and many other reasons and does not always indicate complications. Cm. " " .
Pain in the lower abdomen can be a sign of a threatened miscarriage or a pathological pregnancy (ectopic), but it can also be a normal variant. A pregnant woman's stomach hurts even more often than a non-pregnant woman, and there are reasons for this.
From the first weeks of pregnancy, a surge of hormones occurs, the uterus begins to grow, intestinal motility changes, which often causes pain. The uterus is a muscular organ that periodically contracts, and the longer the pregnancy, the more often this happens. Not all women feel uterine contractions, but some feel slight pain or discomfort during this time.
If pain during pregnancy is irregular, does not increase in strength and frequency, is not cramping and is not accompanied by bloody discharge, then most likely it does not pose a danger. Cm. " " .
Treatment for threatened miscarriage.
Most miscarriages are due to a problem with the fetus. During conception, a malfunction occurs and the embryo turns out to be genetically defective, which most often is an accident and does not depend on the health of the parents. Naturally, if there is a threat of miscarriage in the case of genetic defects, no medications will help and the pregnancy will be terminated.
Many studies have been conducted in different countries of the world and it has already been proven that conservation therapy for the threat of miscarriage in the early stages does not exist. The exception is cases of repeated spontaneous miscarriages, when there is a specific reason for terminating the pregnancy, for example, insufficiency of the second phase of the cycle (see ““). After 20 weeks, tocolytic therapy is used to prolong pregnancy.
In developed countries, progesterone and other drugs are practically not used to treat the threat of miscarriage in the early stages, and women with spotting are simply reassured, offered to rest, and limit physical activity and sex life. If there is a threat of interruption in the early stages, they are sent to the hospital only with increasing bleeding or severe pain. At the same time, the level of pregnancy losses in developed countries is no more than in our country.
In the post-Soviet space, when doctors make a diagnosis of “threatened miscarriage,” often without any justification, they intimidate the pregnant woman, worsen her psychological state and prescribe unnecessary, and sometimes harmful, medications.
Of course, drug treatment can lead to a decrease or disappearance of pain, a decrease in bleeding, but this does not improve the outcome of pregnancy. The bleeding may stop and the uterus will stop contracting, but the genetically defective embryo will still die.
Symptoms may disappear, and the pregnancy at a certain stage will simply stop developing. Such treatment only interferes with the independent removal of the defective ovum and increases the risk of instrumental intervention in the uterus.
If a woman had spotting in the first 12 weeks and the pregnancy ended successfully, this does not mean that the treatment helped. It’s just that the pregnancy was normal and it would have ended with the birth of a healthy child without drugs. Sometimes progesterone or antispasmodics play the role of a placebo and maintain pregnancy on a psychological level.
Threatened miscarriage in the early stages: what to do.
The main thing is a positive psychological attitude. Stress increases bleeding and can contribute to miscarriage. It is important to remember that spotting and abdominal pain during pregnancy may be normal.
It is necessary to consult a doctor, rule out serious pathologies, trophoblastic disease, ectopic pregnancy (see “ “), and calmly continue to carry the pregnancy to term.
Even with partial detachment of the ovum, it is possible to maintain pregnancy. Detachment of the ovum along the edge is accompanied by termination of pregnancy only in 7% of cases.
Clinical studies have shown that bed rest in the early stages is not effective in maintaining pregnancy. However, it is necessary to exclude physical activity and sexual activity.
Staying in a hospital is also not always justified; it is extra stress for a woman. Constant monitoring is usually required for increasing spotting, bleeding, or acute pain.
If the embryo is defective, the pregnancy will be terminated. If conception occurs normally, then it is important for the woman not to be nervous, so as not to provoke pregnancy loss. Most pregnant women, despite the repeated threat of miscarriage, safely carry their babies to term.